MP4/M4A Format Preferences allow you to set how output MP4/M4A files are encoded. This tab will enable you to configure the MP4/M4A Codec, Bit Rate Mode, Bit Rate, Bit Depth, Compression Level, Sample Rate, and Channels.
To open the MP4/M4A Format Preferences tab, choose ‘Preferences’ in the Application Menu and select the Format tab.
- MP4/M4A Codec
- Bit Rate Mode
- VBR Quality
- Bit Rate
- Sample Rate
- Channels
- Bit Depth
- Compression Level
- Extension
MP4/M4A Codec
The list of supported codecs that can be used when converting to MP4/M4A format:
- AAC-LC (Low Complexity AAC) - This is the most efficient and widely used AAC profile, designed for high-quality encoding of music and voice. AAC-LC provides transparent, near-CD quality at 80 kbps for mono and 128 kbps for stereo input. This codec is selected by default.
- AAC-HE v1 (High-Efficiency AAC v1) - This is the extension of AAC, which improves audio quality at lower bit rates, where AAC-LC cannot achieve acceptable quality. This codec is targeted to medium-quality encoding at bit rates of 24 kbps per channel and higher. AAC-HE v1 is 30% more efficient than AAC-LC. However, it is not a replacement for AAC-LC, but rather an extension of it, and should serve as an audio codec for mobile and broadcasting.
- AAC-HE v2 (High-Efficiency AAC v2) - This is the extension of AAC, which improves audio quality at lower bit rates, where AAC-LC cannot achieve acceptable quality. This codec improves audio quality for stereo signals at low bit rates, such as 32 kbps for stereo input. HE-AAC v2 uses Parametric Stereo technology and is 50% more efficient than AAC-HE v1. AAC-HE v2 should be used for mobile, broadcasting, and other domains where CD quality is not essential.
- ALAC (Apple Lossless Audio Codec) - This is the only lossless codec natively supported by iTunes and iOS devices. Users who want to use lossless audio with metadata support in iTunes must use this codec. Audio files compressed with ALAC are about 40% to 60% the size of the originals, depending on the kind of audio.
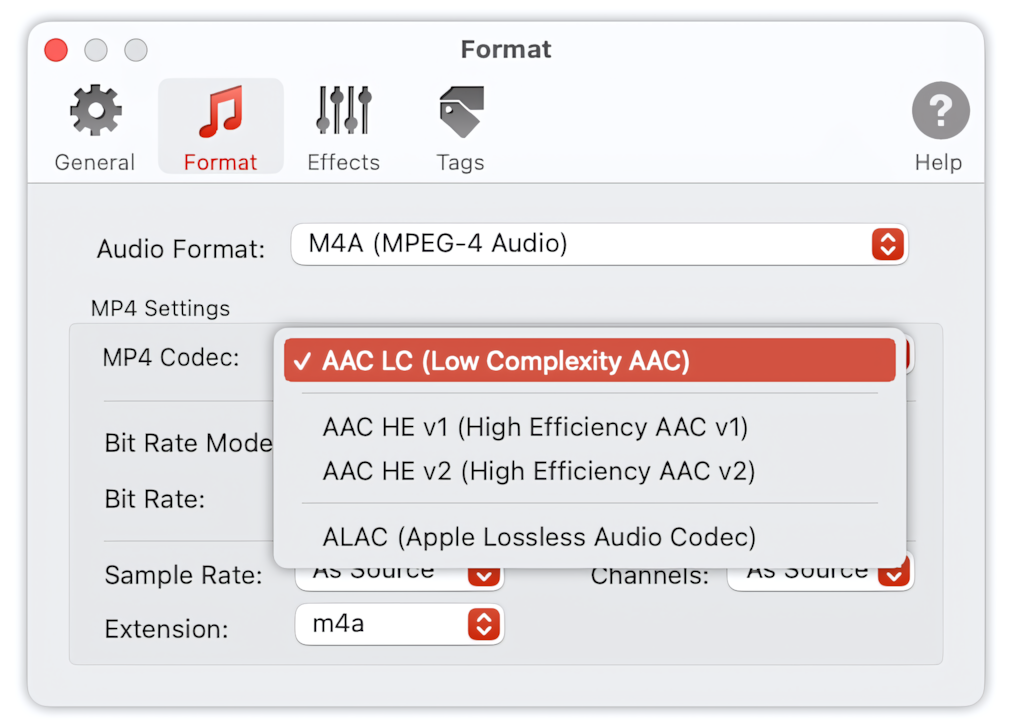 To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Preferences - List of Supported Audio Codecs
To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Preferences - List of Supported Audio Codecs
Bit Rate Mode
The list of supported Bit Rate Modes:
- Constant - recommended for constant-bit-rate network transmission when decoding in real-time, with a fixed end-to-end audio delay. However, due to strict constant bit rate constraints, this mode results in lower audio quality and higher complexity than other encoding modes.
- Average - recommended for controlling file size. Unlike Constant mode, this mode does not provide a constant delay when using constant bit rate transmission; however, it offers nearly optimal global quality while still allowing for strict control over the resulting file size. This mode is selected by default.
- Variable - recommended for controlling the audio quality. The audio signal is encoded with constant quality and virtually no bit rate constraints. This is the best mode to achieve consistent audio quality with the lowest overall bit rate.
Bit Rate Mode is not applicable and has no effect when the Apple Lossless Audio Codec is selected.
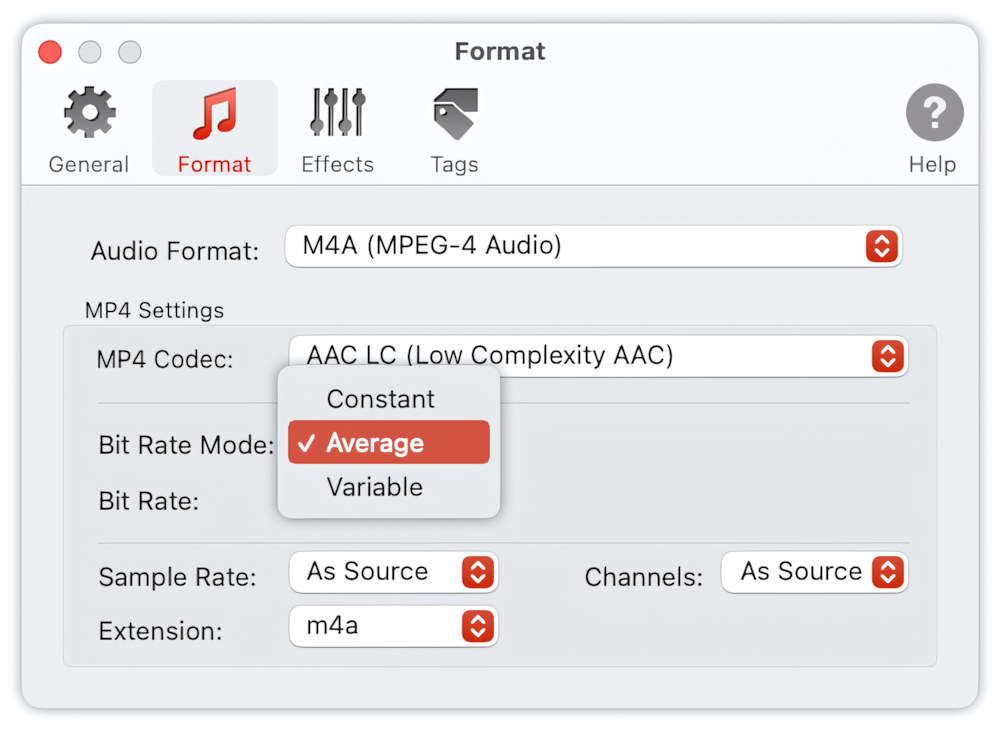 To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Preferences - List of Supported Bit Rates
To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Preferences - List of Supported Bit Rates
VBR Quality
VBR Quality is applicable only when one of the AAC codecs is selected and Bit Rate Mode is Variable. Allows selecting an algorithm that encodes audio with the best quality or the best speed.
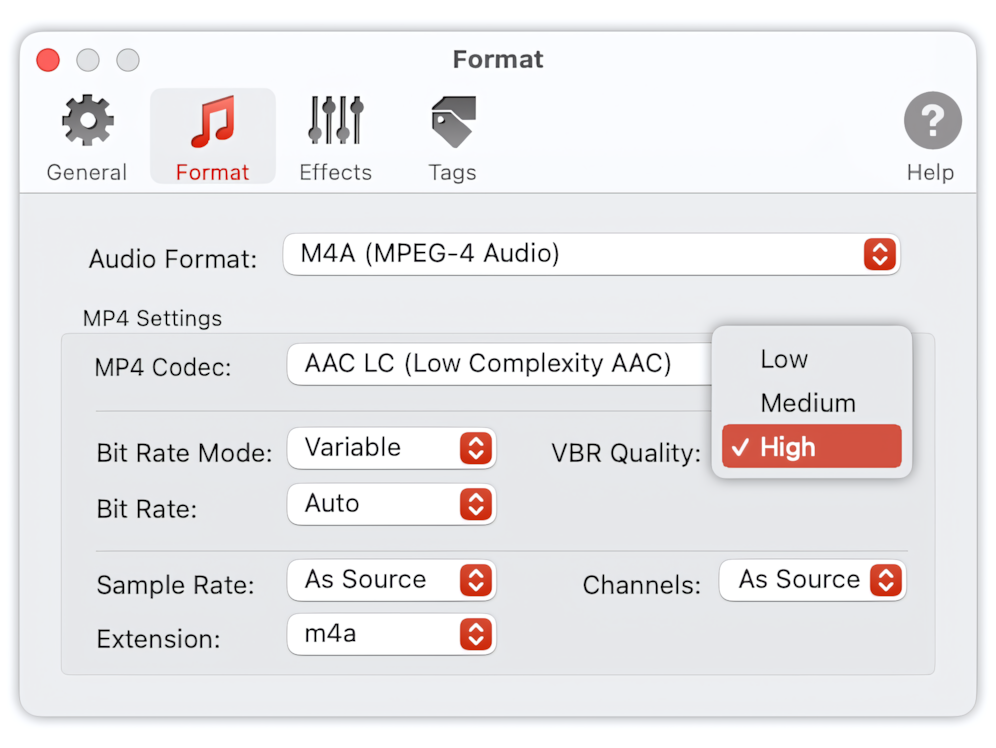 To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Preferences - VBR Quality
To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Preferences - VBR Quality
Bit Rate
The higher the bit rate, the better the quality; however, higher bit rates result in larger files. 'Auto' allows the application to calculate the optimal bit rate for encoded audio based on the source file's bit rate. ‘Auto' is selected by default.
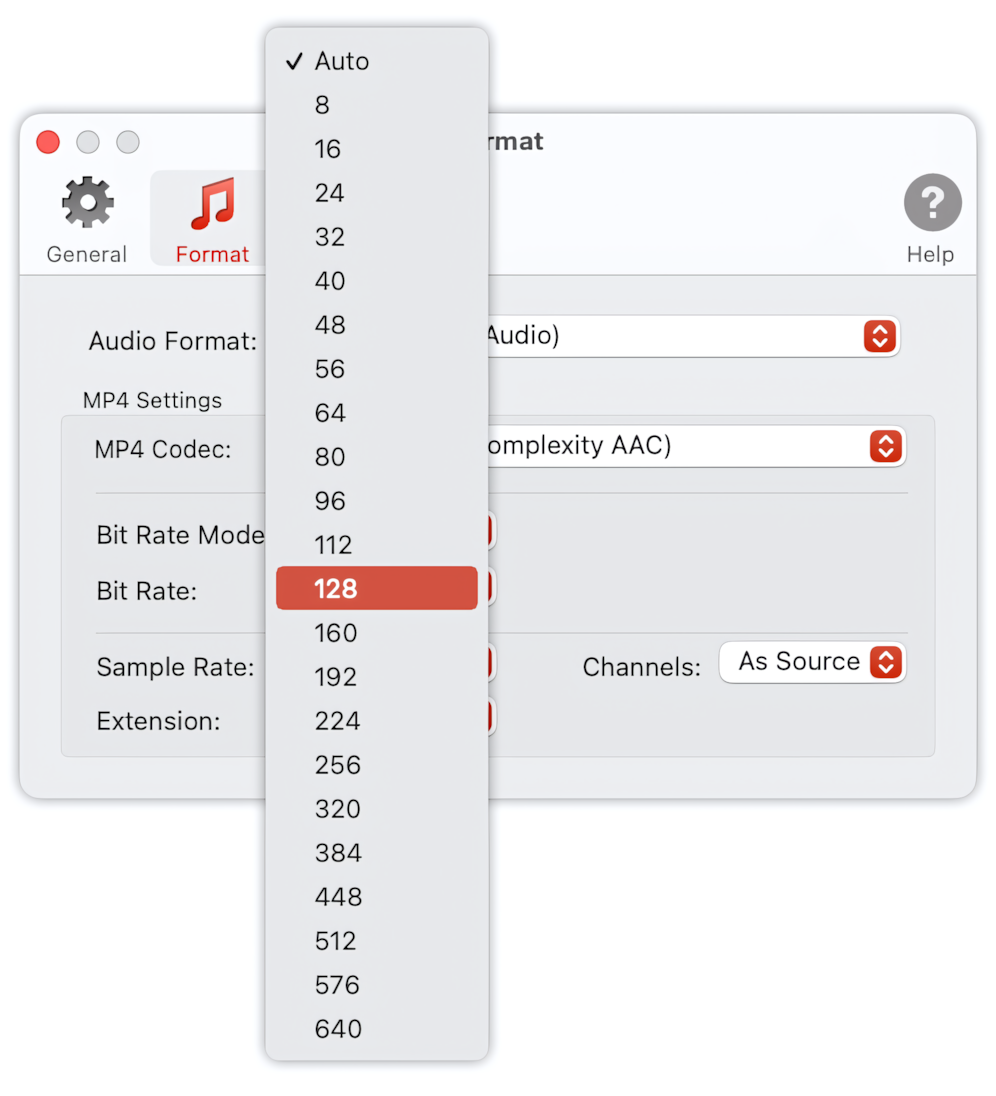 To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Preferences - List of Supported Bit Rates
To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Preferences - List of Supported Bit Rates
Sample Rate
Select ‘As Source’ when encoded audio should have the same sample rate as the source audio. This is the default preferred setting.
A fixed Sample Rate can also be set from 8000 to 384000 Hz, depending on the selected M4A Codec. If the Sample Rate of the source audio differs from the fixed Sample Rate, the output audio will be resampled.
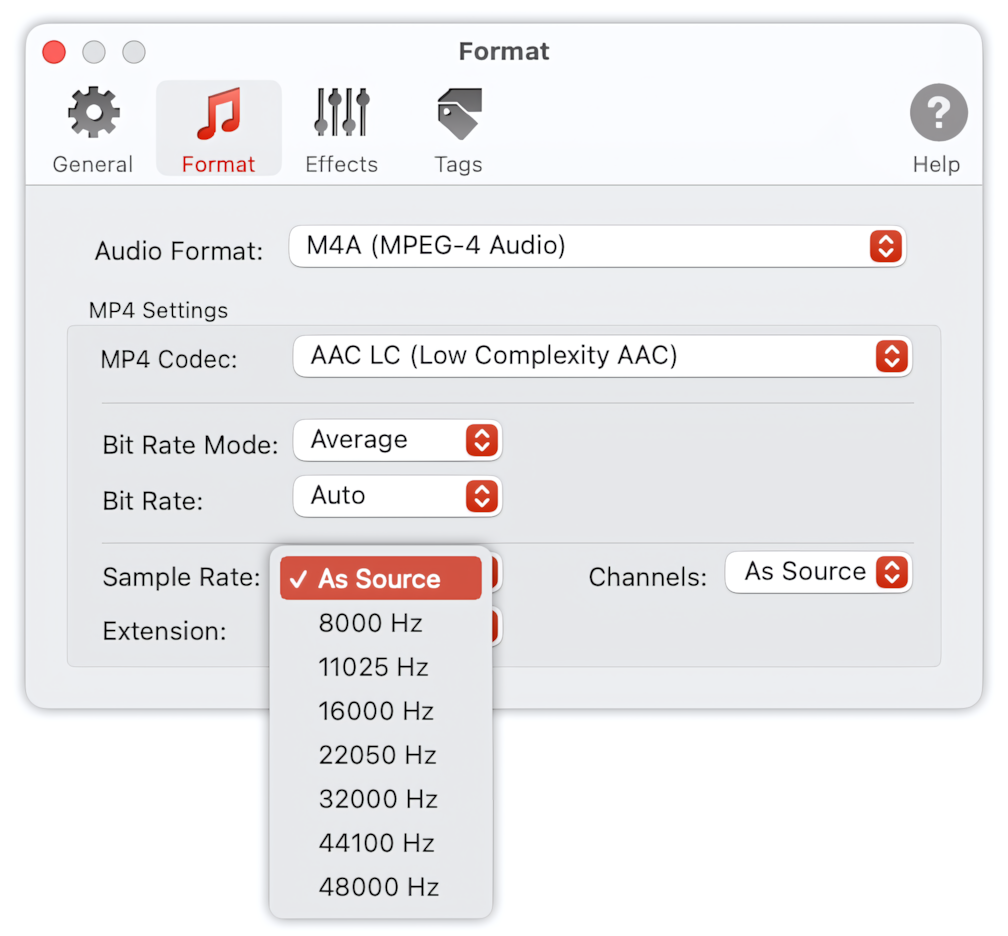 To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Format Preferences - List of Supported Sample Rates
To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Format Preferences - List of Supported Sample Rates
Channels
Select ‘As Source’ when encoded audio should have the same number of channels as the source audio. This is the default preferred setting.
A fixed number of channels can also be set to:
- Mono (1 Channel). If the source audio has more than one channel, it will be downmixed to a mono channel.
- Stereo (2 Channels). If the source audio has more than two channels, it will be downmixed to a stereo format.
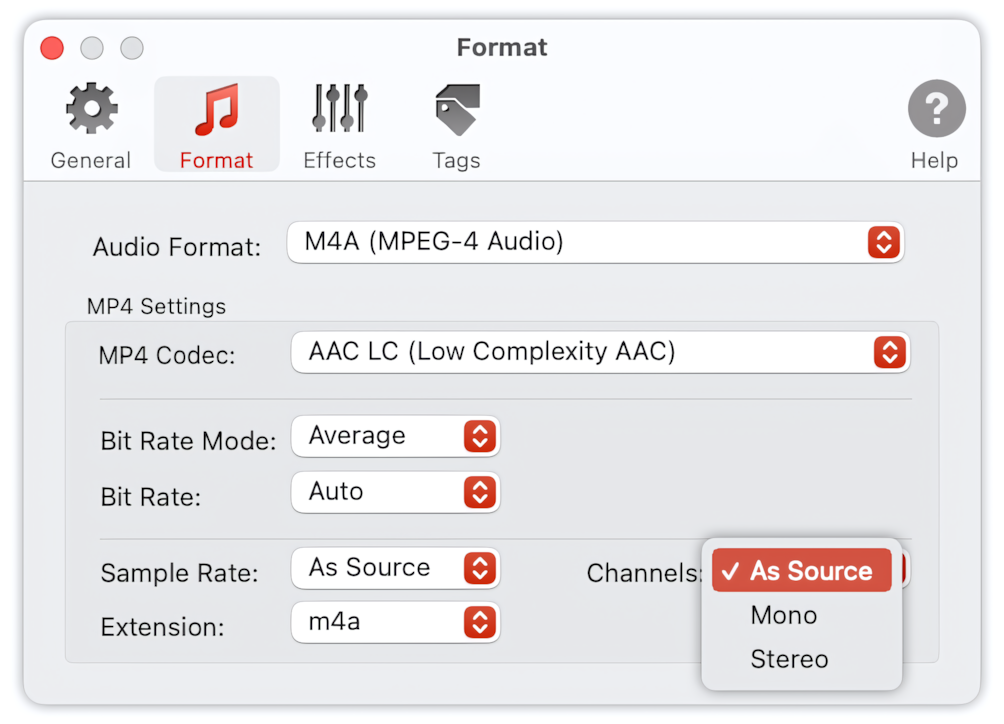 To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Format Preferences - List of Channels
To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Format Preferences - List of Channels
Bit Depth
Select ‘As Source’ when the Bit Depth should be assigned to 16, 24, or 32 bit, depending on the bit depth of the source audio. ‘As Source’ is the default preferred setting. Bit Depth is applicable only when ALAC (Apple Lossless Audio Codec) is selected.
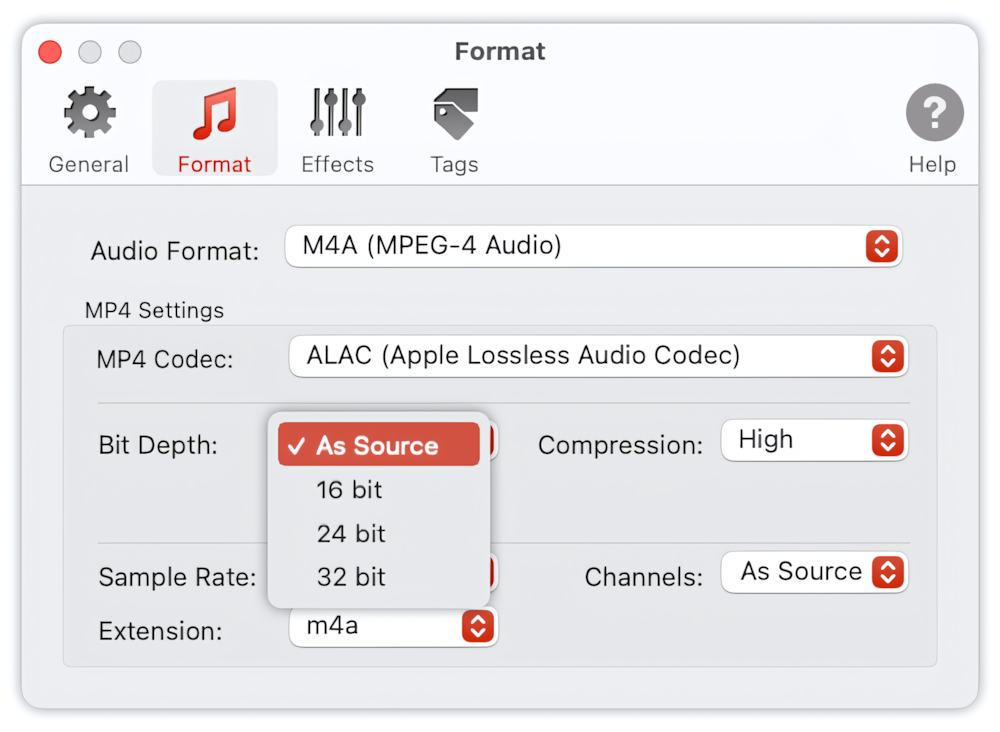 To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Format Preferences - List of Supported Bit Depths
To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Format Preferences - List of Supported Bit Depths
Compression Level
Specifies the value of the compression level and selects the algorithm that provides the best compression with the optimal speed. The default setting is ‘High’, which means the highest compression level is in use. The Compression Level is applicable only when ALAC (Apple Lossless Audio Codec) is selected.
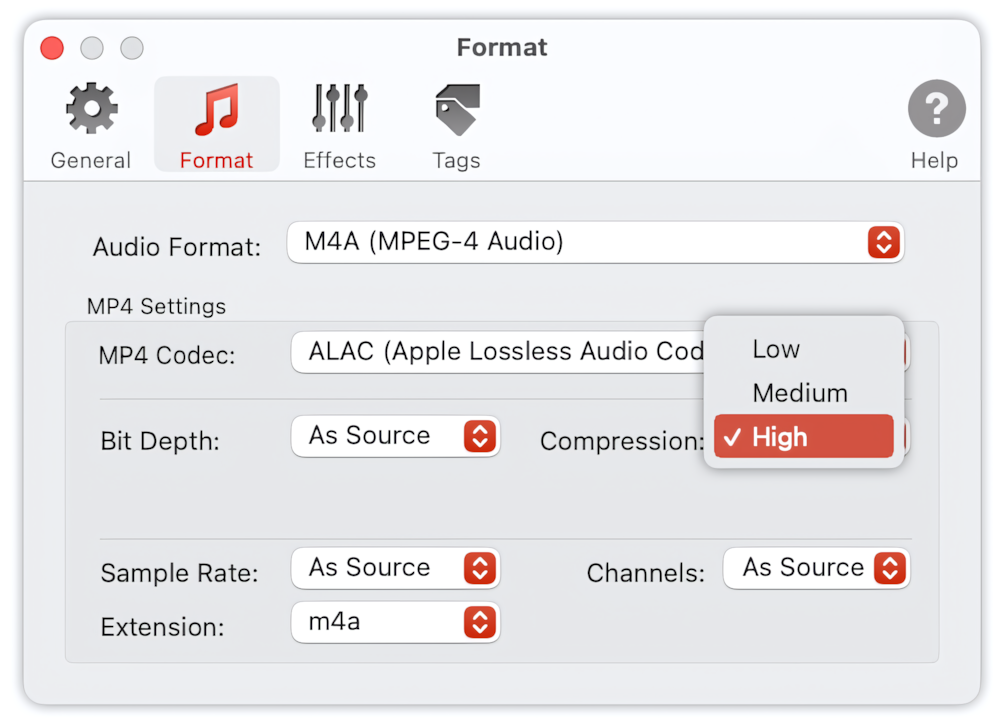 To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Format Preferences - List of Supported Compression Levels
To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Format Preferences - List of Supported Compression Levels
Extension
Specifies the extension of output files - mp4 or m4a.
MP4 stands for MPEG-4. MP4 is a format commonly used to store video, audio, subtitles, and still images. MP4 is also a filename extension used to represent both audio and video files.
M4A stands for MPEG-4 Audio and is a filename extension to represent audio-only MP4 files. MPEG-4 files can contain any number of audio, video, and subtitle streams, making it impossible to determine the type of streams in an MPEG-4 file solely by its extension. As a response to this issue, Apple started using and popularizing the .M4A filename extension. M4A is used for MP4 containers with audio encoded with Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) or Apple Lossless (ALAC) codecs.
 To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Format Preferences - List of Supported Extensions
To Audio Converter - MP4/M4A Format Preferences - List of Supported Extensions
